The world is still catching its breath after the COVID-19 pandemic caused by the coronavirus. But behind the scenes, a far more silent threat is looming—superbugs.
Drug-resistant microbes rarely make headlines, but they’re quietly evolving — and could spark a health crisis worse than any viral pandemic.
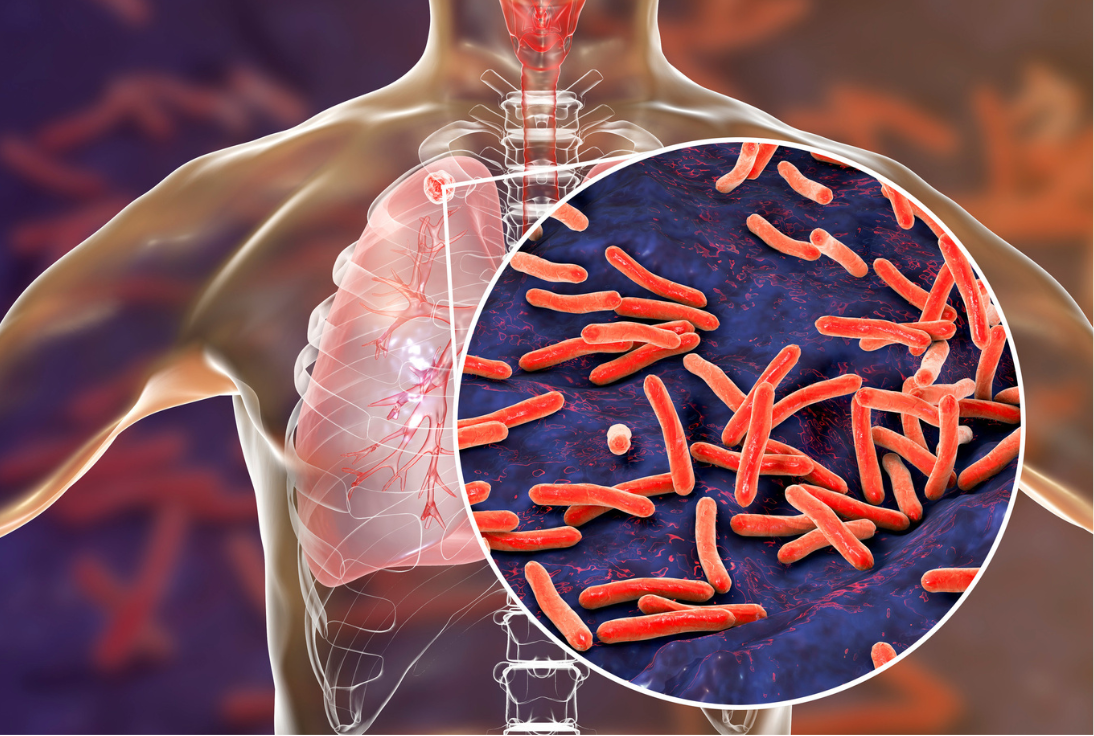
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that primarily affects the lungs. It is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, an acid-fast, rod-shaped bacterium. Common clinical symptoms include:
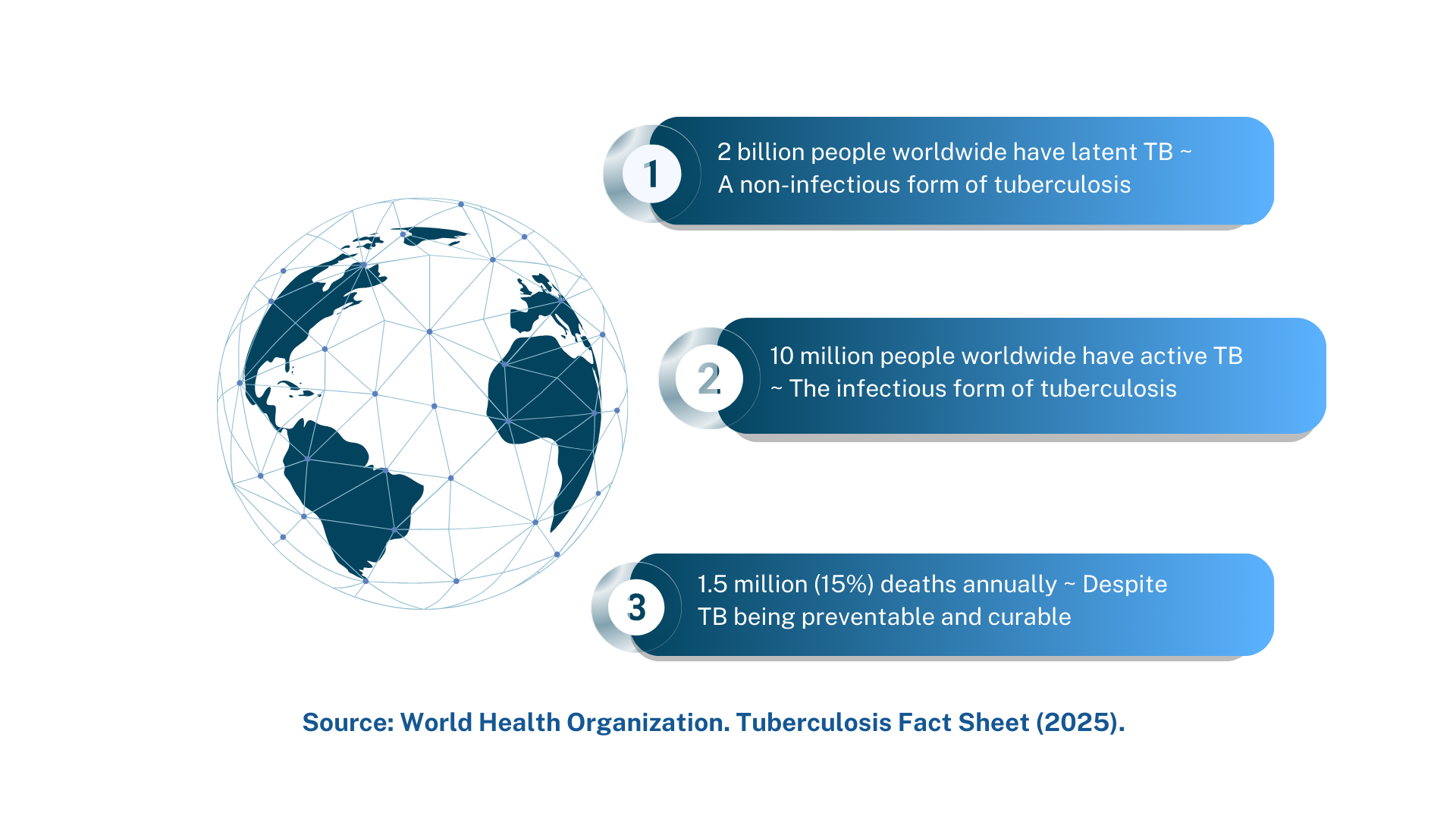
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a major global health concern. An estimated 2 billion people worldwide carry latent TB, a non-infectious form of the disease, while approximately 10 million people suffer from active TB, which is infectious. Despite being both preventable and curable, TB causes around 1.5 million deaths annually.
(Source: World Health Organization, Tuberculosis Fact Sheet, 2025)
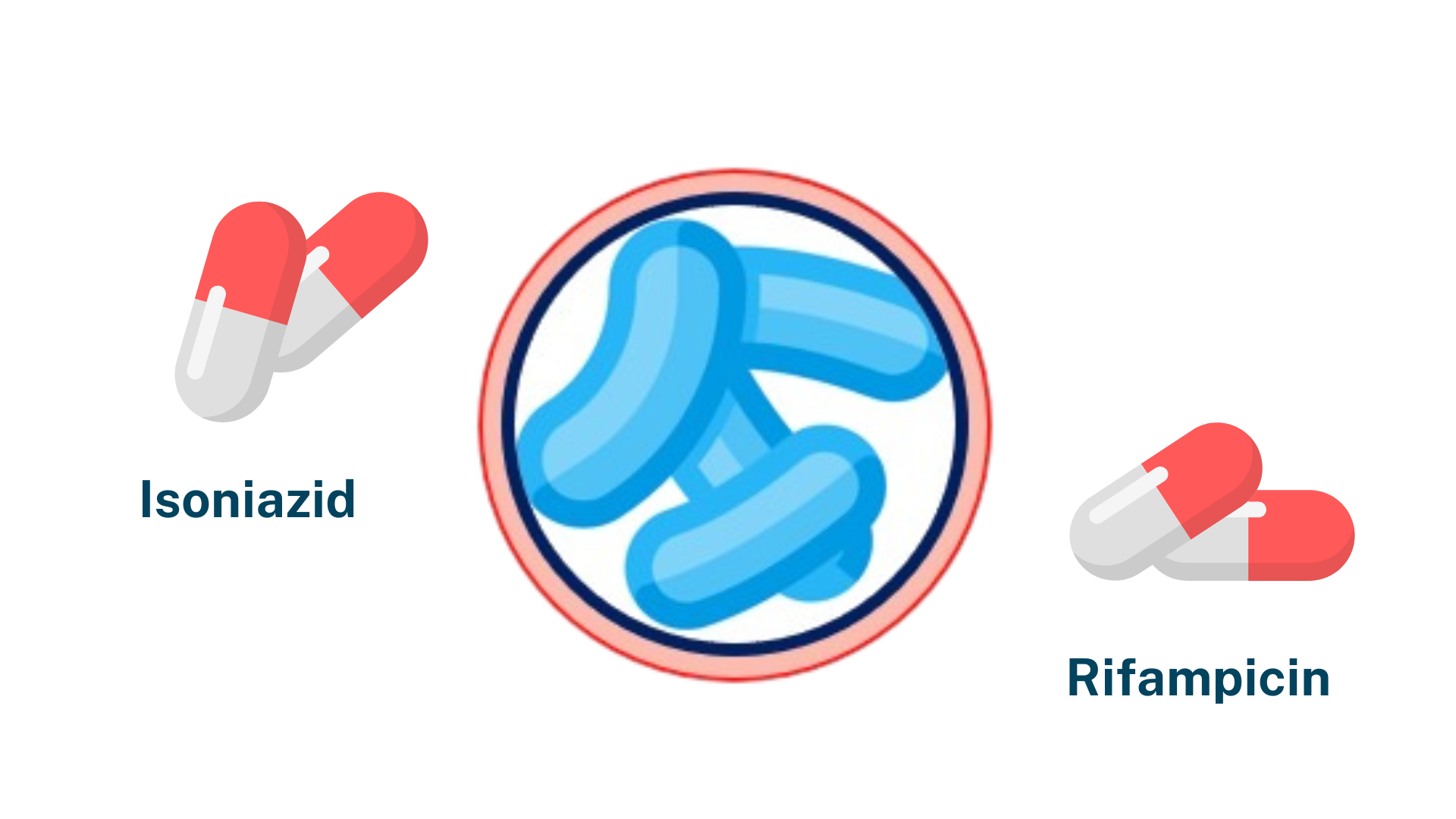
This is due to multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MDR-TB), which is resistant to Isoniazid and Rifampicin.
These two antibiotics are among the most powerful first-line anti-TB medications, making MDR-TB a significant public health concern.
Multidrug resistance develops due to:
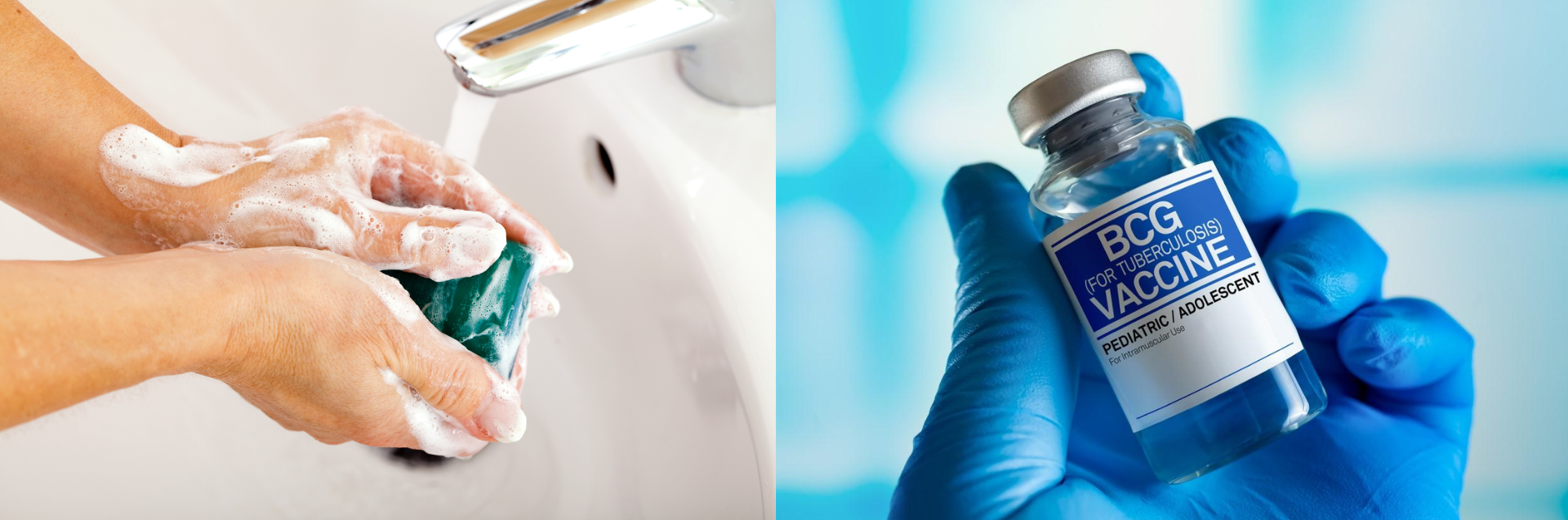

Although antibiotic resistance occurs naturally, human actions can strongly influence its spread. We can help slow resistance by:
The article is prepared by Biorism Scientist, Dr. Woon JJ, (PhD in Microbiology).